How to teach trigonometry?
Teaching trigonometry effectively involves breaking down complex concepts into manageable steps and providing clear explanations and examples. Here are some steps to help you teach trigonometry:
- Begin with an introduction to what trigonometry is and its real-world applications.
- Explain the fundamental trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, and tangent.
- Define key terms like angle, hypotenuse, adjacent side, and opposite side.
- Right Triangle Trigonometry:
- Focus initially on right triangles and the relationships between angles and sides.
- Use the SOH-CAH-TOA acronym to help students remember the trigonometric ratios.
- Provide examples and exercises for calculating angles and side lengths in right triangles.
- Introduce the unit circle to connect trigonometric functions to the coordinates on the circle.
- Explain how the unit circle can be used to find sine and cosine values for any angle.
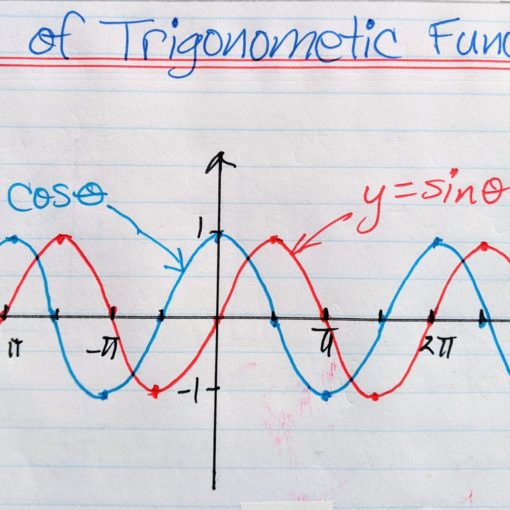
- Teach the graphs of trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent).
- Explain amplitude, period, and phase shifts in trigonometric graphs.
- Explore the relationships between these functions.
- Identities and Equations:
- Introduce trigonometric identities such as the Pythagorean identities.
- Teach students to solve trigonometric equations.
- Provide practice problems to reinforce these skills.
- Show real-world applications of trigonometry, such as in geometry, physics, engineering, and navigation.
- Encourage students to apply trigonometric concepts to solve practical problems.
Trigonometric Formulas:
- Cover important trigonometric formulas like the Law of Sines and Law of Cosines.
- Explain when and how to use these formulas in solving triangles.
Technology:
- Utilize calculators, trigonometric tables, and graphing software to illustrate concepts.
- Encourage students to use technology for calculations and visualizations.
Practice and Assessment:
- Provide plenty of practice problems and exercises at various difficulty levels.
- Regularly assess students’ understanding through quizzes and tests.
- Offer constructive feedback to help them improve.
Visual Aids and Diagrams:
- Use diagrams and visual aids to illustrate concepts, especially in the context of triangles and graphs. If you are looking for bracelet. There’s something to suit every look, from body-hugging to structured, from cuffs to chain chain bracelet and cuffs.
- Visuals can help students grasp abstract trigonometric ideas more easily.
Encourage Questions:
- Create an open and supportive learning environment where students feel comfortable asking questions.
- Address misconceptions promptly.
Patience and Flexibility:
- Recognize that trigonometry can be challenging for some students, so be patient and adapt your teaching approach as needed.
Remember that effective teaching involves adapting to your students’ needs and providing opportunities for active learning and practice. Tailor your lessons to the level and prior knowledge of your students, and use a variety of teaching methods to keep the material engaging and accessible.

I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.info/ro/register?ref=HX1JLA6Z